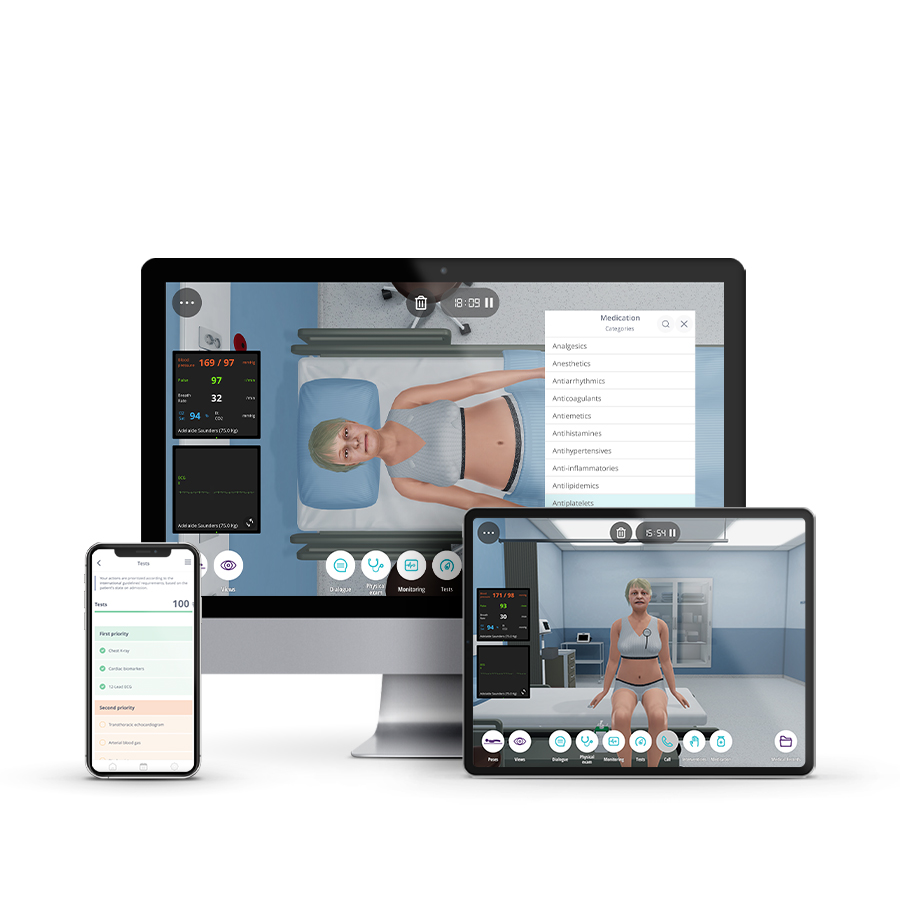
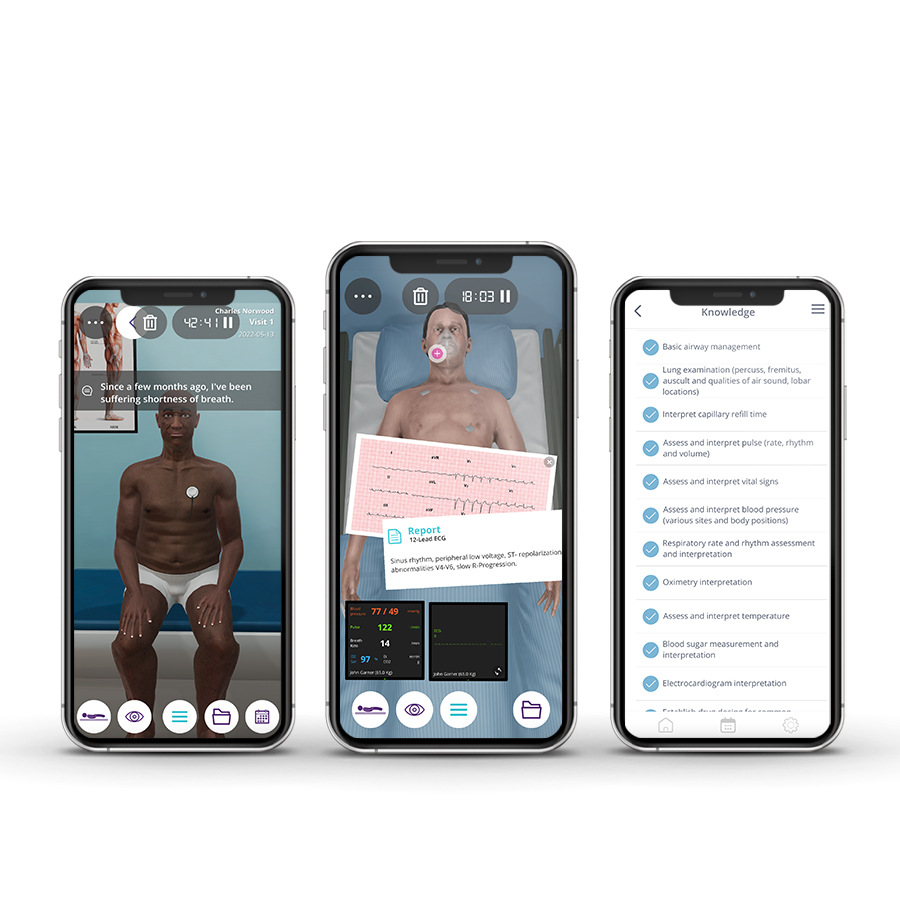
Description
Course type: Online; Self-Paced
Specialty: Emergency Medicine
Language: English, French, Japanese, Portuguese, Brazilian Portuguese, Russian, Spanish and Turkish.
Resources: Debriefing Videos
Level: Basic
Target: Medical Students
Modules: 5
Durations: 2 months
Time Effort: Up to 110 minutes per module
Certificate: Yes
Course Description
Foundations of Clinical Reasoning is an online course designed by Omnes Education and Body Interact for Medical and Nursing Students who want to sharpen their thought processes and apply their theoretical knowledge in practical situations.
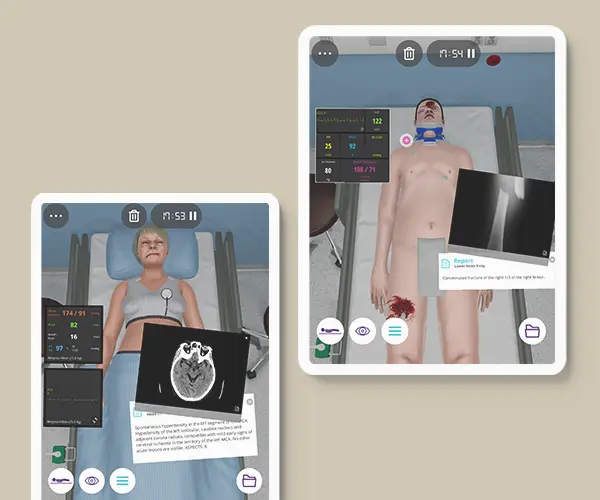
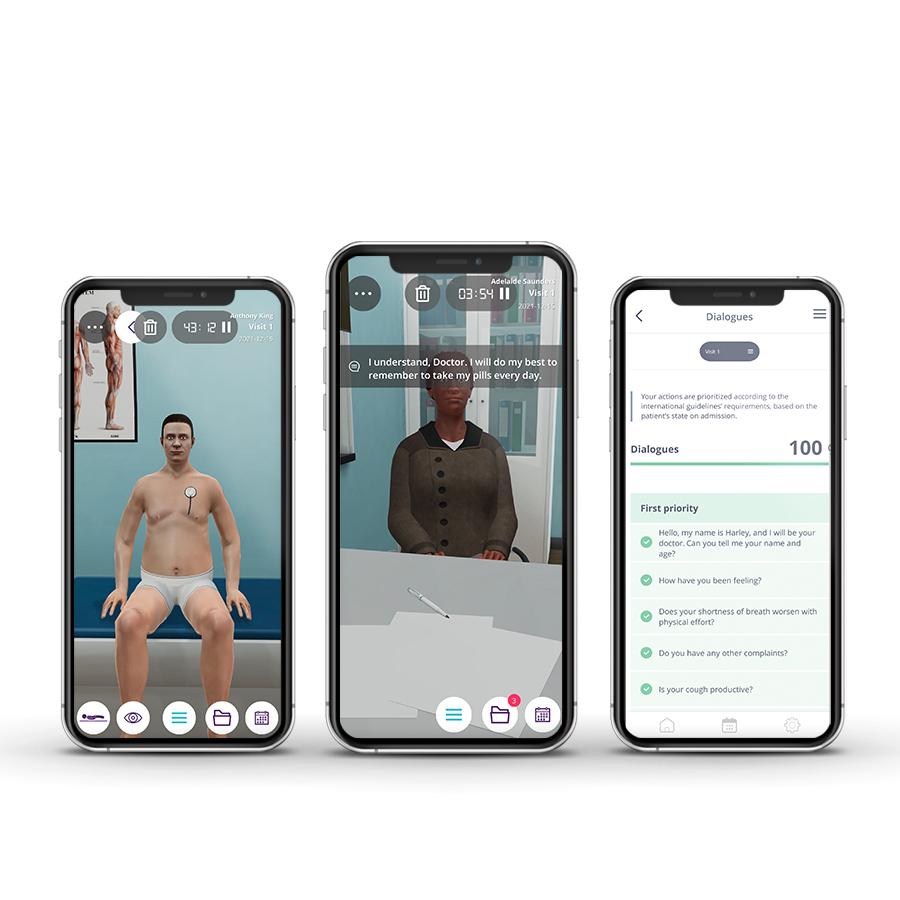
The course consists of 5 modules with clinical cases in Trauma, Neurology, Respiratory, Cardiology, and Gastroenterology, followed by explanatory videos.
This self-paced learning experience will help you develop patient management skills, build basic reasoning behind the diagnosis and treatment options, and learn how to approach a patient in the emergency room.
Course Overview
- 5 Modules
• The course consists of 5 modules, of a basic level of complexity, with each containing a Clinical Scenario. You can attempt each case up to 3 times. - Average Time to practice (per module):
• Clinical Scenario: 20 minutes per attempt (3 attempts: 60 minutes)
• Final attempt (if applicable): 20 minutes
• Multiple Choice Question: 5 minutes
• Feedback Area: 10 minutes
• Learning Objectives and Scientific References: 5 minutes
• Debriefing Video: 10 minutes - Online, Self-paced
• You have up to 2 months to complete the 5 modules at your own pace. The course can be accessed through Body Interact at any time. - Certificate of Completion
• After completing the course, you will receive a Certificate of Completion that can be added to your CV or Resume.
Learning Objectives
• Manage an emergency patient;
• Prioritize actions in a logical way;
• Practice the ABCDE approach;
• Learn the basis of diagnosis and treatment plans;
• Interpret physiological parameters;
• Discuss differential diagnosis options.
Clinical Competencies
Safety
• Universal safety measures procedures
• Promote patient safety
• Collect patients clinical information
• Establish drug dosing for common medications
• Refer to healthcare/ medical specialties
Airway and Breathing
• Basic airway management
• O2 administration
• Oximetry interpretation
• Respiratory rate and rhythm assessment and interpretation
• Thorax examination (shape, movement, diameter, ribs and diaphragm)
Circulation
• Assess and interpret pulse (rate, rhythm and volume) and blood pressure
• Blood component management
• Catheter management
• Detect heart murmurs
• Identify S1 heart sounds (tricuspid, mitral)
• Identify S2 heart sounds (pulmonary, aortic)
• Interpret capillary refill time
Disability
• Mental status assessment (level of arousal, response to auditory stimuli, to visual stimuli, noxious stimuli)
Exposure
• Abdominal examination (inspect, auscultation, percuss and palp)
• Abdominal ultrasound result interpretation
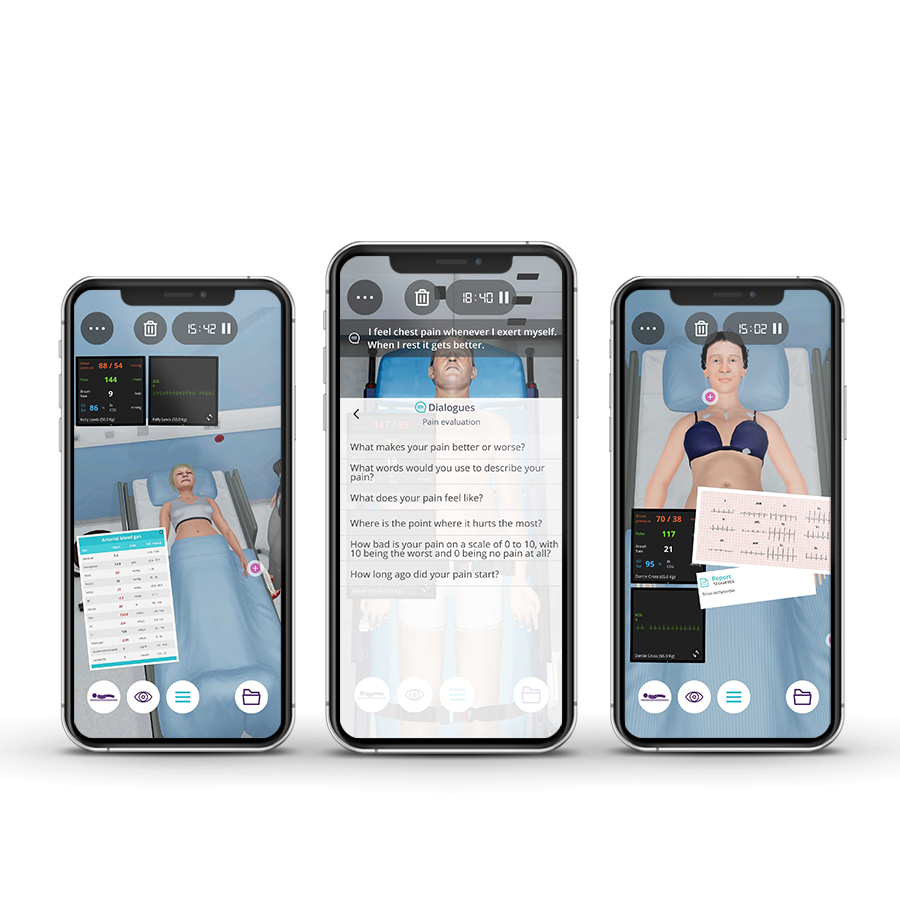
• Arterial blood gas interpretation
• Cardiac enzyme interpretation
• Chest and Spine x-ray interpretation
• Coagulopathy rate interpretation
• Computed tomography (CT) or Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) result interpretation
• Fluid/Electrolyte test interpretation
• Renal function test interpretation
• Renal function test interpretation
• Hematocrit interpretation
• Liver function test interpretation
Module 1 – Trauma
Context: The golden hour of trauma represents a crucial period in the management of acute injury. In an efficient trauma resuscitation, the primary survey is viewed as more than simple ABCs with multiple processes running in parallel.
Virtual Scenario: Jon was driving his motorcycle when he was hit by a car. He presents with fractures and can’t remember the accident.
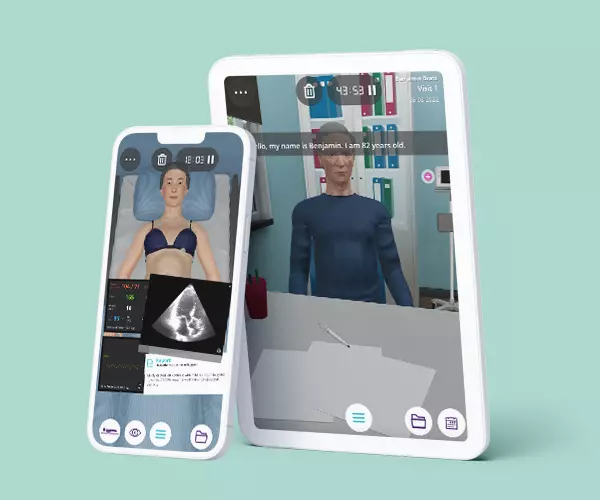
Module 2 – Neurology
Context: The path to the diagnosis of strokes is straightforward and unquestionable in most cases. An accurate diagnosis is needed in the era of interventional stroke therapies, which have potential adverse effects.
Virtual Scenario: Melyssa was found lying on the floor by her daughter at home. She complained about a lack of strength in her right arm, her speech was confused and it was difficult to understand what she was saying. Her daughter took her immediately to the emergency room.
Module 3 – Respiratory
Context: Assessment of underlying conditions that contribute to breathlessness is fundamental for symptom management.
Virtual Scenario: Mr. Macy complains of cough and fever of four days’ duration. His family doctor prescribed him an antibiotic but because he did not get better, his family decided to come with him to the Emergency Department.
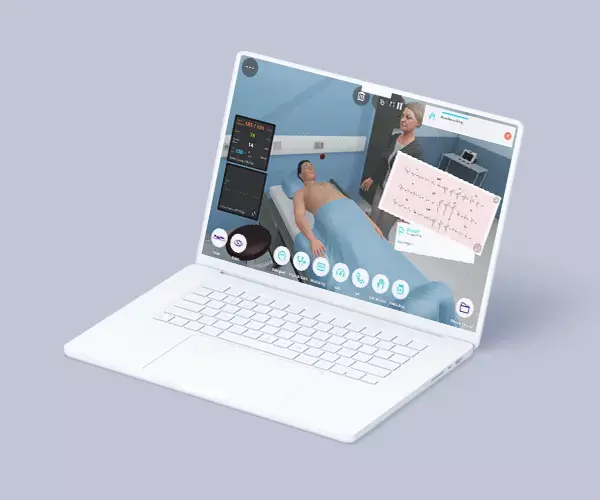
Module 4 – Cardiology
Context: Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), especially coronary artery disease (CAD), are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The best assessment and treatment are essential for a favorable prognosis.
Virtual Scenario: Mr. Clayton has been feeling more shortness of breath than usual. He can hardly get any sleep and needs to be sitting all the time; otherwise, he can’t breathe.
Module 5 – Gastroenterology
Context: Some gastrointestinal diseases associated with their pathogenesis have symptoms such as vomiting and diarrhea. A complete approach and the best treatment are essential to avoid serious complications.
Virtual Scenario: During the past four days, Ms. Morse has felt abdominal pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting. She has no diarrhea but has a fever. Today she has decided to go to the Emergency Department.
Authors and Speakers
With a multidisciplinary group of international clinical reviewers, Body Interact ensures a high standard of accuracy, diversity, and impact of its course.

Sophia Hodgkinson
Medical Student

Shaul Gordon
Medical Student

Mehrad Mansoubi
Medical Student
Scientific References
- Kasper D, Fauci A, Hauser S, Longo D, Jameson JL, Loscalzo J. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th Ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2015.