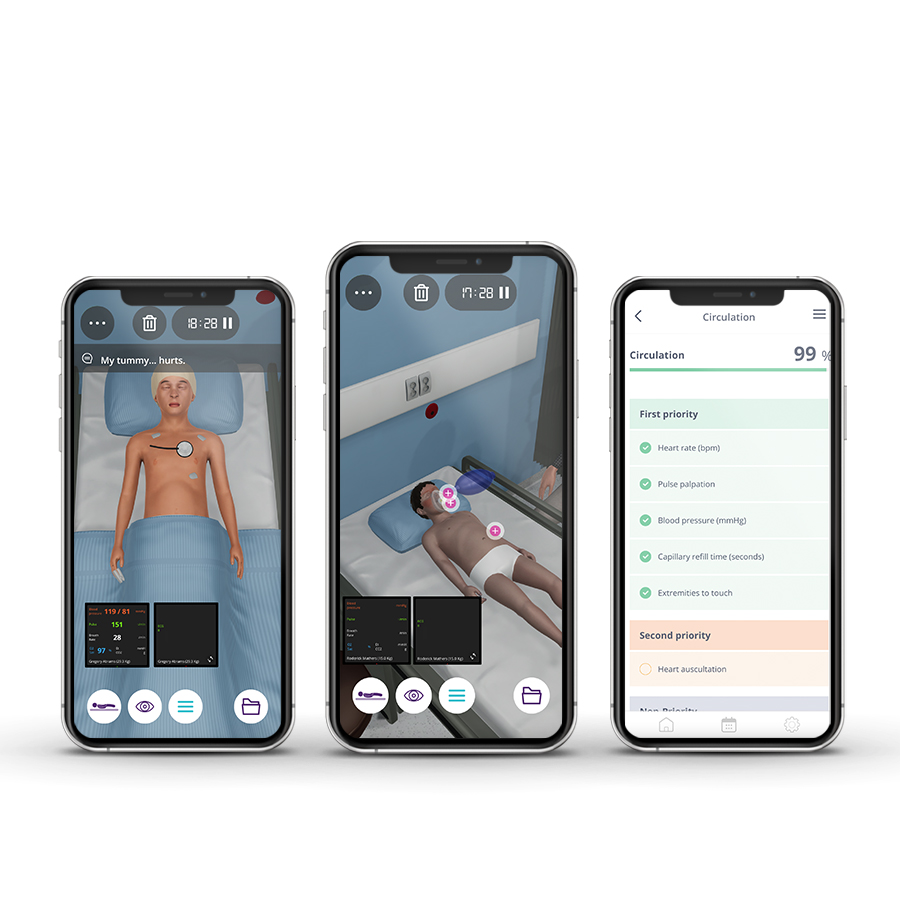
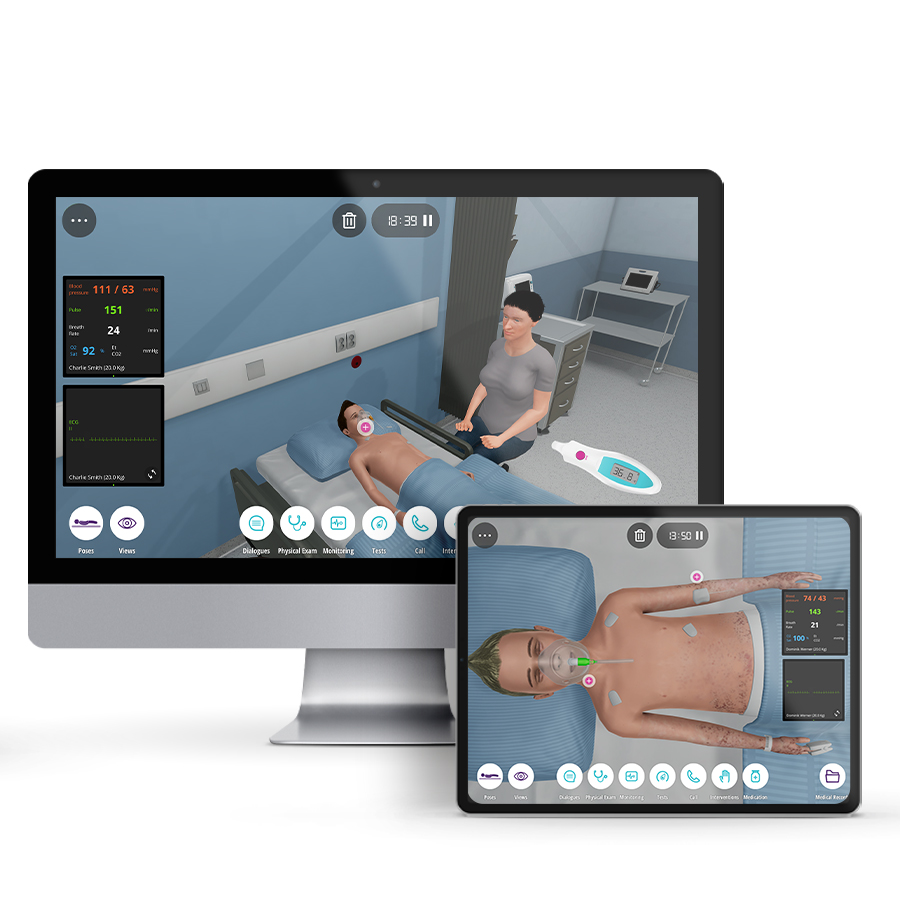
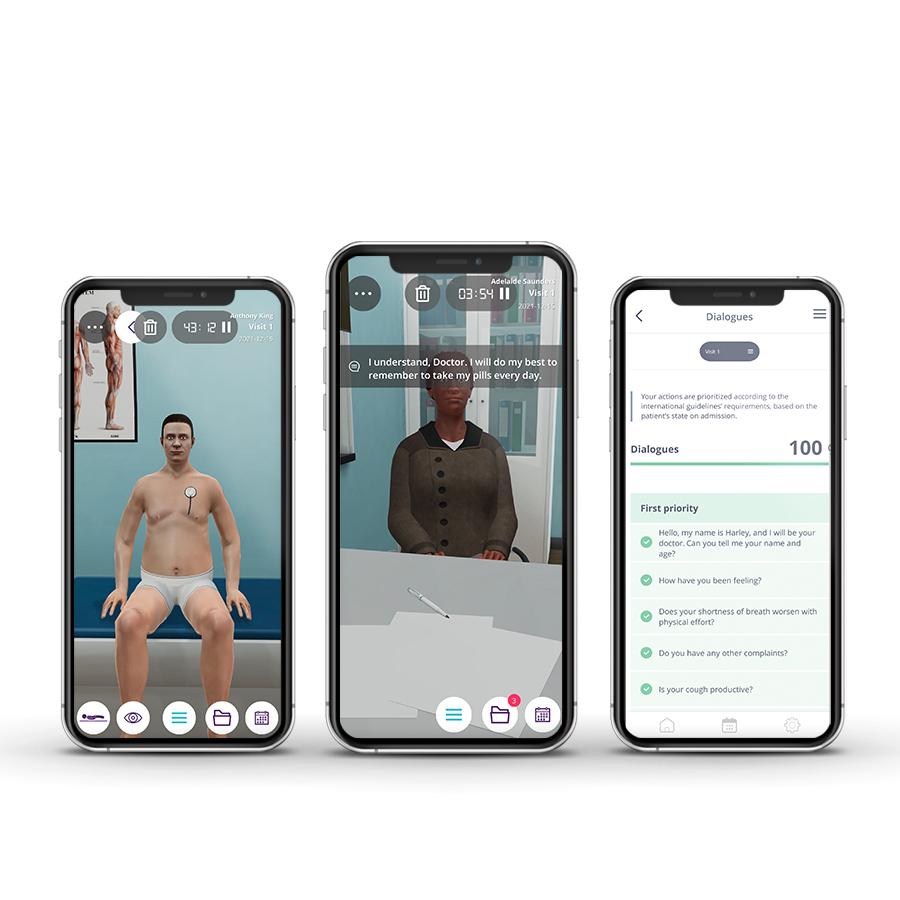
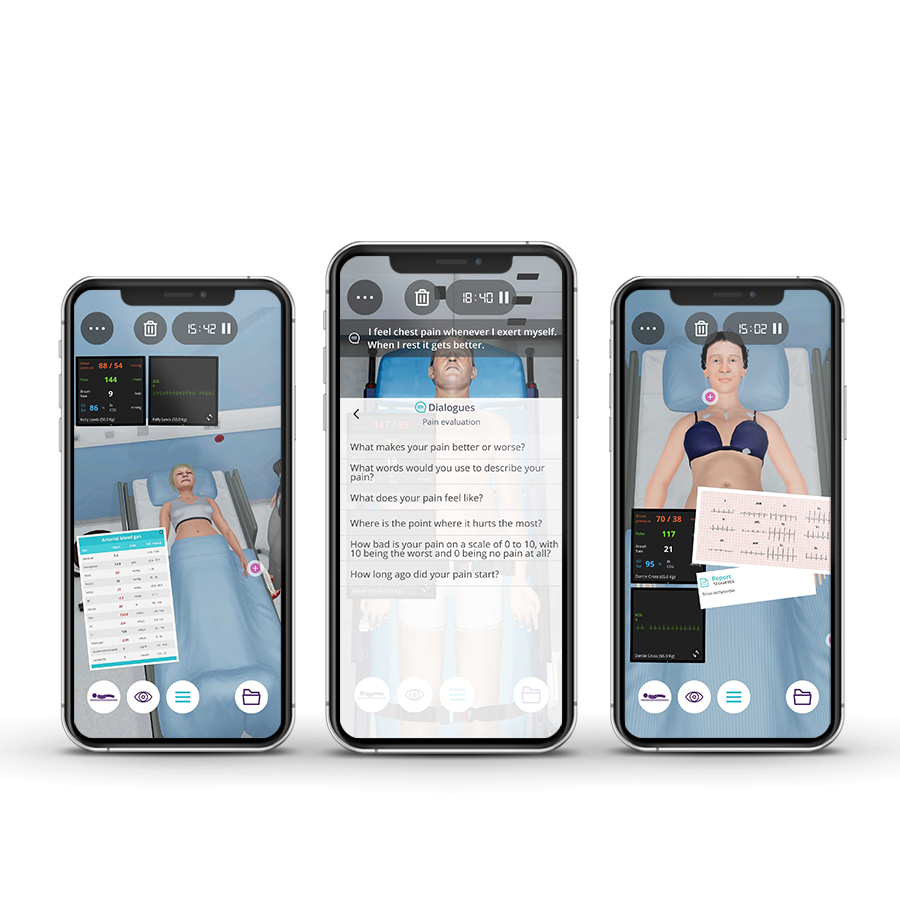
Description
Course type: Online; Self-Paced
Specialty: Pediatrics
Language: English / Portuguese
Level: Intermediate
Target: Medical Students
Modules: 5
Durations: 2 months
Time Effort: Up to 110 minutes per module
Certificate: Yes
Course Description
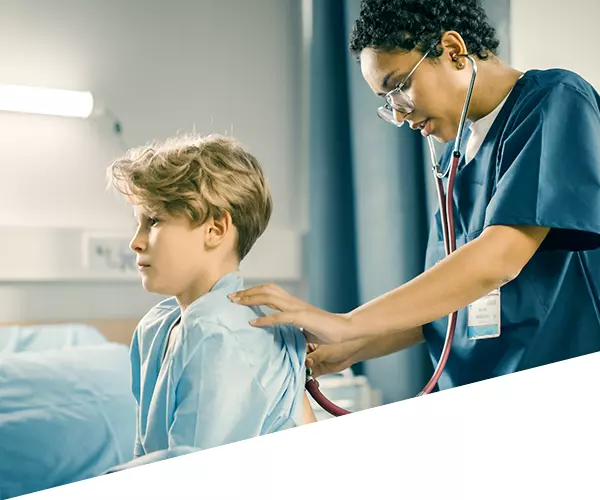
Emergency medicine in pediatrics focuses on the need to make immediate decisions and to act quickly to prevent complications, severe disabilities, or even the death of the patient. Emergency Pediatricians provide immediate recognition, assessment, care, and stabilize acute illnesses and injuries. To accomplish this, high pressure and fast pace is a constant requirement, as well as a broad knowledge base and a variety of well-developed clinical competencies and technical skills.
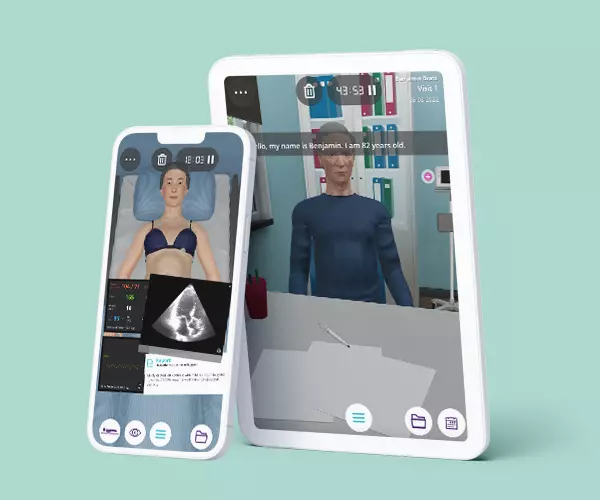
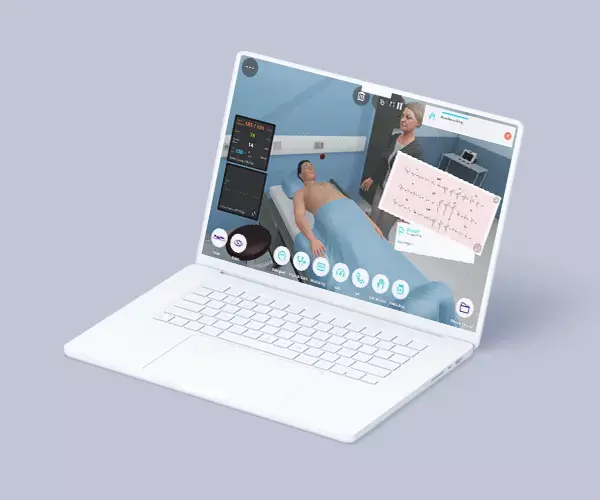
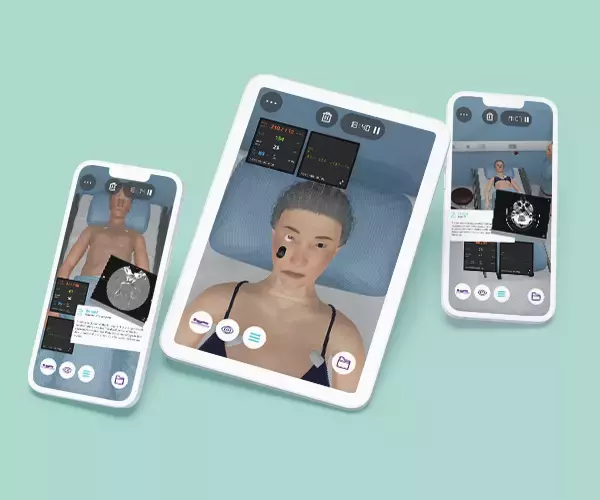
The Pediatrics Emergencies course aims to provide future residents with a solid foundation of practice based on virtual patients’ scenarios. It includes five clinical scenarios from different specialties ((toxicology, cardiology, respiratory, endocrinology, and neurology) with a diverse population of pediatric patients.
Course Overview
- 5 Modules
• The course consists of 5 modules, with each containing a Clinical Scenario. You can attempt each case up to 3 times. - Average Time to practice (per module)
• Clinical Scenario: 20 minutes per attempt (3 attempts: 60 minutes)
• Final attempt (if applicable): 20 minutes
• Multiple Choice Question: 5 minutes
• Feedback Area: 10 minutes
• Learning Objectives and Scientific References: 5 minutes
• Debriefing Video: 10 minutes - Online, Self-paced
• You have up to 2 months to complete the 5 modules at your own pace. The course can be accessed through Body Interact at any time. - Certificate of Completion
• After completing the course, you will receive a Certificate of Completion that can be added to your CV or Resume.
Learning Objectives
• Perform the adequate approach to a pediatric drug overdose
• Perform the adequate approach to tachycardia
• Identify and treat acute respiratory illness
• Identify and treat diabetic ketoacidosis associated with hypovolemic shock
• Perform the clinical approach to a septic shock
Clinical Competencies
Safety
• Universal safety measures procedures
• Promote patient safety
• Collect patients clinical information
• Establish drug dosing for common medications
• Refer to healthcare/ medical specialties
Airway and Breathing
• Basic airway management
• O2 administration
• Oximetry interpretation
• Respiratory rate and rhythm assessment and interpretation
• Thorax and Lung examination (shape, movement, diameter, ribs and diaphragm)
Circulation
• Assess and interpret pulse (rate, rhythm and volume) and blood pressure
• Blood component management
• Catheter management
• Detect heart murmurs
• Interpret capillary refill time
• Cardiac defibrillation
Disability
• Mental status assessment (level of arousal, response to auditory stimuli, to visual stimuli, noxious stimuli)
• Pupillary examination
Exposure
• Abdominal examination (inspect, auscultation, percuss and palp)
• Venous blood gas interpretation
• Complementary diagnostic test interpretation
Module 1 – Non-responsive child
Context: A Pediatric Emergency Physician is an expert caring for children with acute illnesses or injuries. This specialist is trained to treat a wide range of problems, such as involuntary intoxications, which require immediate medical help. These problems are usually serious and can put a child’s life at risk.
Virtual Scenario: Roderick has been a seemingly healthy child since birth. One day, he was playing at his grandmother’s house and became extremely sleepy during the afternoon. His grandmother found him lying down, barely breathing, and called an ambulance.
Module 2 – Suddenly the child felt sick as the child was getting ready to go to school
Context: At rest, younger children have a faster heartbeat than older children. Nevertheless, heart rate variability may occur. When there is an abnormally fast heartbeat unrelated to physical activity or age, it may be due to an abnormality in the heart’s electrical system.
Virtual Scenario: Alexandra suddenly felt ill when she was getting ready to go to school. Her mother noticed and rushed her daughter to the Pediatric Emergency Unit.
Module 3 – Difficult to breathe
Context: Mild breathing changes or problems can commonly occur due to a minor cold or allergies. However, some breathing problems in children – such as wheezing and chest retraction – can be a sign of something more significant that warrants emergency medical care.
Virtual Scenario: Charlie was in kindergarten on what seemed a normal day, playing and interacting with the other children. Suddenly the kindergarten staff noticed his labored breathing and immediately brought Charlie to Hospital.
Module 4 – Child with abdominal pain and vomiting
Context: Metabolic diseases can occur in children with life-threatening complications. The importance of carefully evaluating and monitoring signs and symptoms is crucial to anticipate serious complications. If left untreated, shock can be fatal in children.
Virtual Scenario: Recently, Gregory started to feel abdominal pain accompanied by vomiting. Today his father found him weaker and immediately brought Gregory to the Pediatric Emergency Department.
Module 5 – Confused speech
Context: Septicemia is one of the most dangerous conditions, especially in septic shock. Early diagnosis and intervention with the appropriate pathogen, increases the chance of the child to survive.
Virtual Scenario: Dominik was having a seemingly normal day playing with his brothers when his mother noticed he had a fever. Later that day, he started vomiting and his mother took him to the Hospital.
Scientific References
- Kirkham FJ. Guidelines for the management of encephalitis in children. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013;55(2):107-110.
- Kneen R, Michael BD, Menson E, et al. Management of suspected viral encephalitis in children – Association of British Neurologists and British Paediatric Allergy, Immunology and Infection Group national guidelines. J Infect. 2012;64(5):449-477.
- Bronstein D, Shields W, Glaser C. Chapter 36 Encephalitis and Meningoencephalitis. In: Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. 7th Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier;2014:492-512.
- British National Formulary for Children 2014-2015: the Authority on the Selection and Use of Medicines in Children. London: BMJ Group, Pharmaceutical Press and RCPCH Publications Ltd; 2014.
- Crisp S, Rainbow J. Emergencies in Paediatrics and Neonatology. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2013.
- Flerlage J, Engorn B. The Harriet Lane Handbook – a Manual for Pediatric House Officers. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders / Elsevier; 2015.
- Kreshak AA, Tomaszewski CA, Clark RF, Cantrell FL. Flumazenil administration in poisoned pediatric patients. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28(5):448-450.
- Skellett S, Hampshire S, Bingham R, Maconochie I, Mitchell S. European Paediatric Advanced Life Support. London: Resuscitation Council (UK); 2016.
- Hartman ME, Cheifetz IM. Pediatric Emergencies and Resuscitation. In: Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St Geme JW, Schor NF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016: Chapter 67.
- Horeczko T, Inaba AS. Cardiac Disorders. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018: Chapter 170.
- Skellett S, Hampshire S, Bingham R, Maconochie I, Mitchell S. European Paediatric Advanced Life Support. London: Resuscitation Council (UK); 2016.
- Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. European Respiratory Journal. 2014;43(2):343-373.
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, British Thoracic Society. British Guideline on the Management of Asthma: A National Clinical Guideline. 2016.
- Eber E, Midulla F. ERS Handbook of Paediatric Respiratory Medicine. Sheffield: European Respiratory Society; 2013.
- Nievas IFF, Anand KJS. Severe acute asthma exacerbation in children: a stepwise approach for escalating therapy in a pediatric intensive care unit. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2013;18(2):88-104.
- Perretta JS. Neonatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care: a Patient Case Method. Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company; 2014.
- Skellett S, Hampshire S, Bingham R, Maconochie I, Mitchell S. European Paediatric Advanced Life Support. London: Resuscitation Council (UK); 2016.
- Wilmott R, Bush A, Boat T, Deterding R, Ratjen F, Chernick V. Kendig and Chernick’s Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children. 8th Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2012.
- Evans L, Rhodes A, alhazzani W, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Critical Care Medicine. 2021;49(11):e1063-e1143.
- Topjian AA, Raymond TT, Atkins D, et al. Part 4: Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation. 2020;142:S469-S523.
- Davis AL, Carcillo JA, Aneja RK, et al. American College of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Parameters for Hemodynamic Support of Pediatric and Neonatal Septic Shock. Crit Care Med. 2017;45(6):1061-1093.